Neurological Manifestations of COVID-19 Feature T Cell Exhaustion and Dedifferentiated Monocytes in Cerebrospinal Fluid
Jan 1, 2021·,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,·
0 min read
Michael Heming
Xiaolin Li
Saskia Räuber
Anne K Mausberg
Anna-Lena Börsch
Maike Hartlehnert
Arpita Singhal
I-Na Lu
Michael Fleischer
Fabian Szepanowski
Oliver Witzke
Thorsten Brenner
Ulf Dittmer
Nir Yosef
Christroph Kleinschnitz
Heinz Wiendl
Mark Stettner
Gerd Meyer Zu Hörste
Abstract
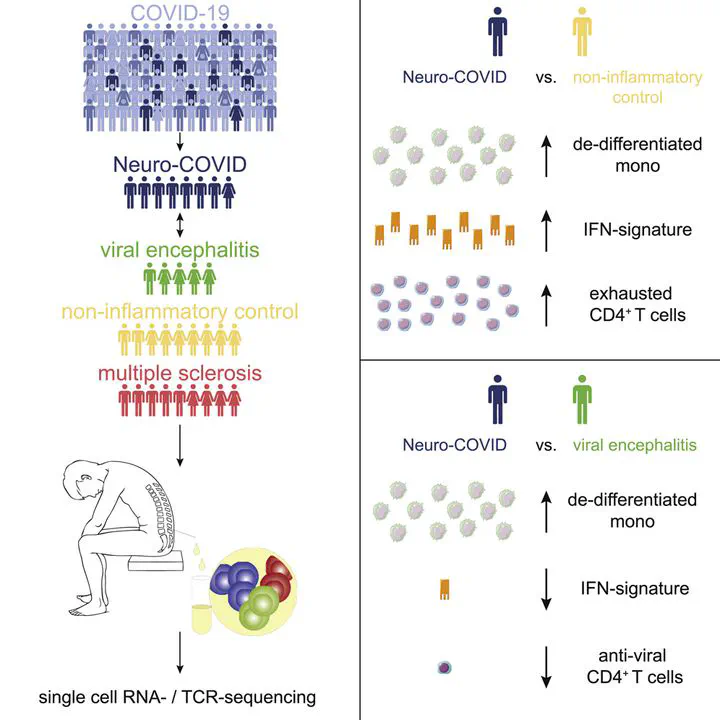
Patients suffering from Coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) can develop neurological sequelae, such as headache, neuroinflammatory or cerebrovascular disease. These conditions - here termed Neuro-COVID - are more frequent in patients with severe COVID-19. To understand the etiology of these neurological sequelae, we utilized single-cell sequencing and examined the immune cell profiles from the cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) of Neuro-COVID patients compared to patients with non-inflammatory and autoimmune neurological diseases or with viral encephalitis. The CSF of Neuro-COVID patients exhibited an expansion of dedifferentiated monocytes and of exhausted CD4+ T cells. Neuro-COVID CSF leukocytes featured an enriched interferon signature; however, this was less pronounced than in viral encephalitis. Repertoire analysis revealed broad clonal T cell expansion and curtailed interferon response in severe compared to mild Neuro-COVID patients. Collectively, our findings document the CSF immune compartment in Neuro-COVID patients and suggest compromised antiviral responses in this setting.
Type
Publication
Immunity