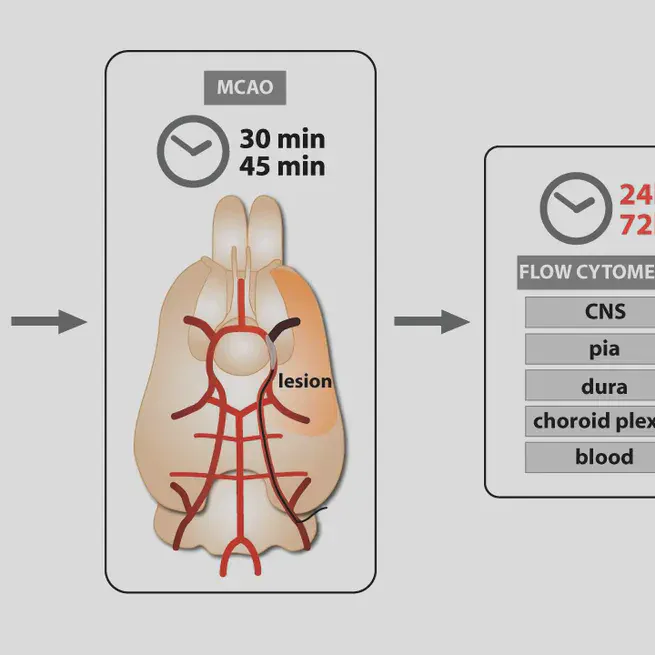
We deeply characterize tissue-resident leukocytes in meninges and brain parenchyma and discover that leukocytes respond differently to stroke depending on their site of residence. We thereby discover a unique phenotype of myeloid cells exclusive to the brain after stroke. These stroke-associated myeloid cells partially resemble neurodegenerative disease-associated microglia. They are mainly of resident microglial origin, partially conserved in humans and exhibit a lipid-phagocytosing phenotype. Blocking markers specific for these cells partially ameliorates stroke outcome thus providing a potential therapeutic target.
Feb 1, 2022
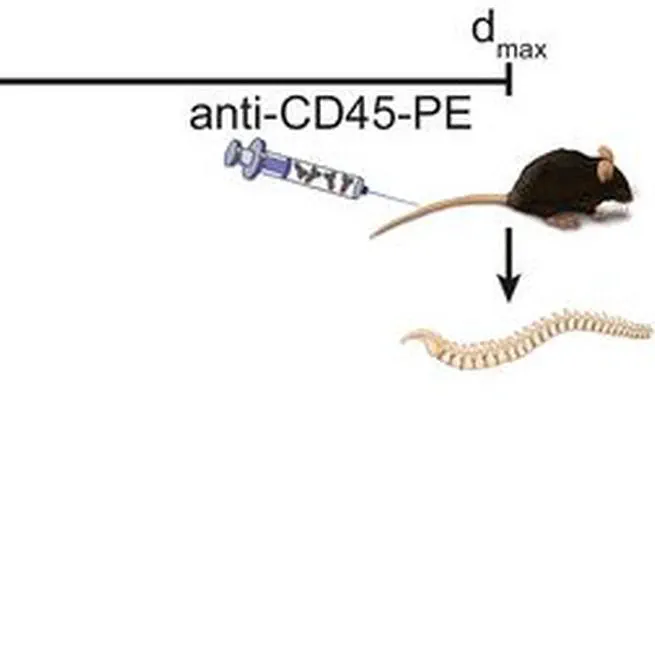
By generating a compartment-specific transcriptional map of meningeal versus parenchymal leukocytes in experimental neuroinflammation, we found a follicular phenotype of meningeal B cells and a corresponding follicular helper-like phenotype in meningeal Th17 cells. The meninges thus instructed a site-specific local phenotype to proinflammatory autoreactive T cells. We identified the transcription factor Bcl6 in Th17 cells to promote interactions with meningeal B cells, isotype-switching, and B cell-supporting chemokines. This may describe a mechanism controlling meningeal autoimmunity and helps understanding how the meninges, as a recently recognized immunologically active site, contribute to autoimmune tissue damage in multiple sclerosis.
Sep 1, 2021
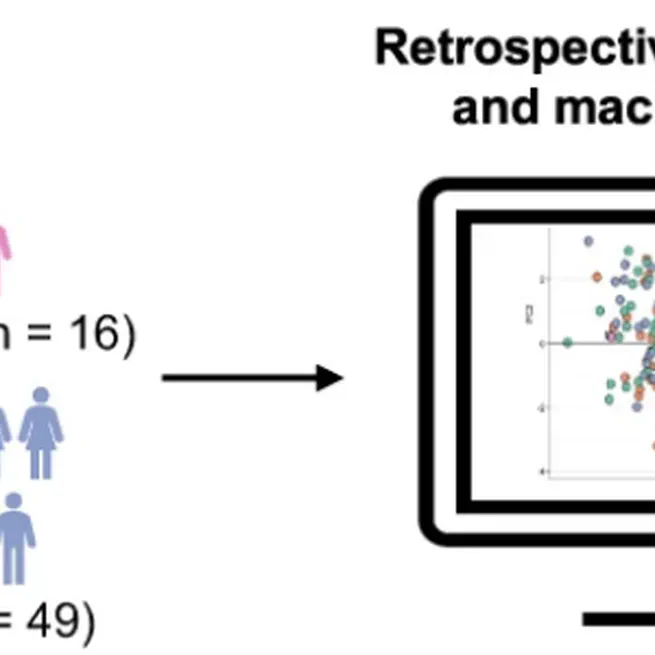
We performed basic CSF analysis and multi-dimensional flow cytometry of CSF and blood cells from 59 patients with primary psychotic disorders in comparison to inflammatory and non-inflammatory controls. We found an expansion of monocytes in the blood and CSF of psychosis patients. A machine learning model incorporating blood and CSF parameters differentated psychosis from non-inflammatory controls better than individual paramaters.
Aug 1, 2021
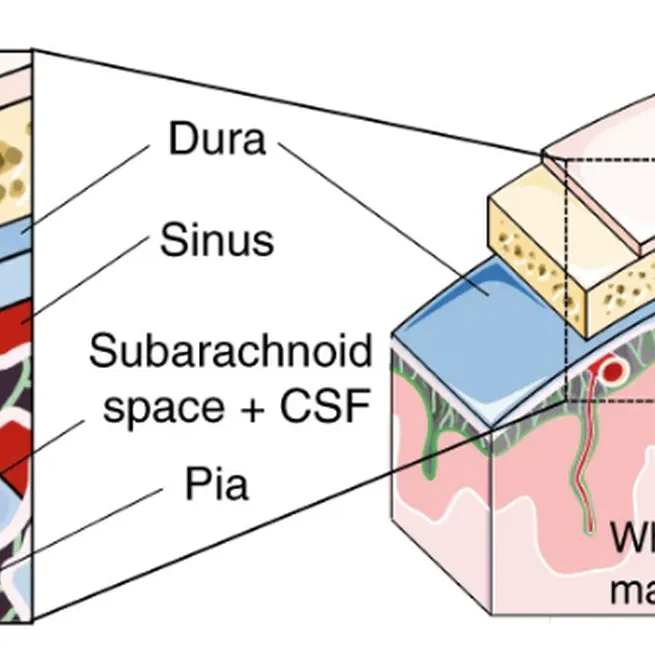
Based on single-cell transcriptomics, we here identify a highly location-specific composition and expression profile of tissue-resident leukocytes in CNS border compartments featuring B cells and their progenitors in the dura as an unexpected site of B cell residence.
Jul 1, 2021
Apr 1, 2020
Jan 1, 2020